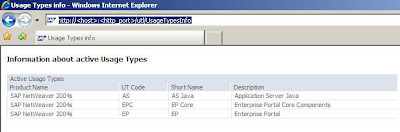
Note that the Usage Types delivered with other tools - like SDM (via manual deployment of corresponding SCAs) - are not presented here.

Note that the Usage Types delivered with other tools - like SDM (via manual deployment of corresponding SCAs) - are not presented here.

How to start the wizard:
2) In the SAP NetWeaver Administrator by following the path System Management -> Configuration -> SPNEGO Configuration Wizard. Steps: 1) Create and configure a service user on the Active Directory Servers (ADS), which act as a Kerberos Domain Controllers (KDC) with the below properties
 3) LDAP settings in Configtool
3) LDAP settings in Configtool
4) Run SPNego wizard
Final Steps:
TEST SSO:
Hit the URL http://host:port/irj/portal, It shoud not ask for username/password.
Add the login module EvaluateTicketLoginModule (or EvaluateAssertionTicketLoginModule) to the login module stacks for the J2EE Engine policy configurations of the application components that accept login tickets for SSO. To do this, use the Security Provider Service of the Visual Administrator.
After you complete the wizard, the ticket-issuing system is shown in the Trusted Systems list. The J2EE Engine accepts logon tickets that have been issued by the corresponding server.
